If you’re looking for a phone system for your business or local office, you have two options to choose from VoIP or landline. Every business, regardless of industry, needs a phone system. Let’s compare VoIP vs Landline.
According to Forbes, as much as 71 percent of leads are wasted due to extended/delayed response times. Statistics show that it takes most businesses two days to return a phone call. A Google study revealed that as much as 70 percent of mobile users click the call feature from their smartphones when they search for a business.
Based on these statistics, it’s clear that having a reliable business phone system should be among your top priorities.
The big questions then are:
- Should you go with landline or VoIP?
- How will VoIP vs. landline impact your business?
In order to help you choose the right phone system for your business, this guide will compare each of the two options in detail.
Here is an overview of what you’ll learn in this in-depth comparison:
- What are VoIP and a landline?
- How each one works
- Pros and cons
- Features
- Cost
- Reliability
- Technology used
What is VoIP?
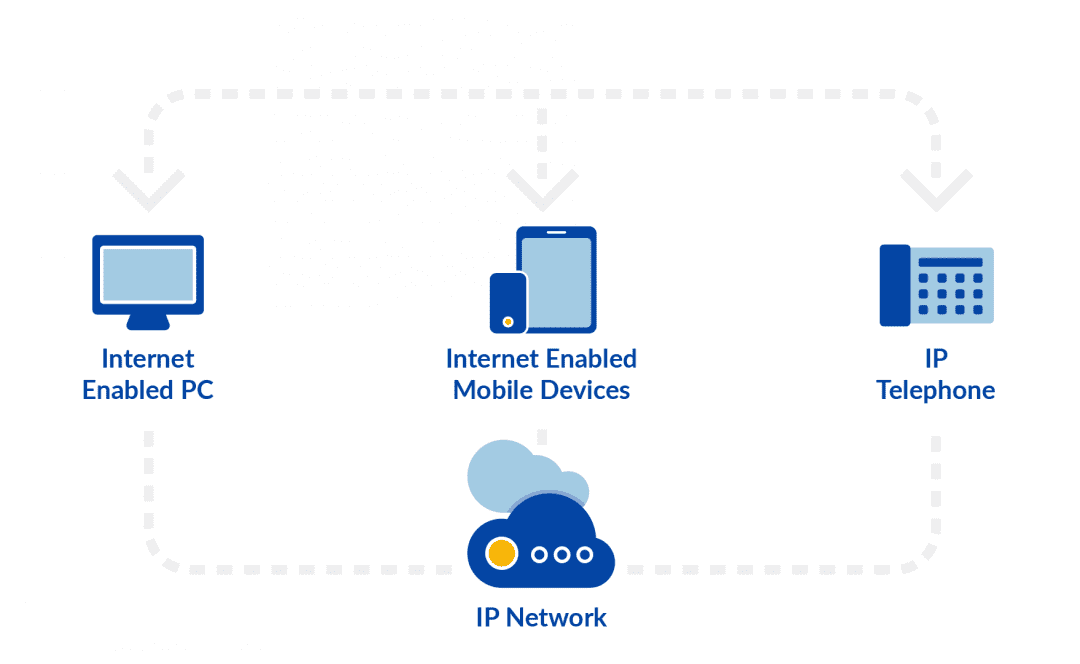
Voice Over Internet Protocol (or VoIP) is also known as Internet calling, IP telephony, voice over network and Internet telephony. Whatever you call it, VoIP uses your Internet connection to make calls. Your voice is transmitted as data over the Internet.
IP telephony isn’t new: the first transmission was sent back in 1973, though the technology was far more limited 40+ years ago.
As the Internet has evolved and become universally available, so has VoIP. The Wall Street Journal reported in 2013 that 25% of U.S. households are now using VoIP in place of their old landlines. Today, businesses all over the world are using it, and it is expected to continue to grow rapidly between now and 2021.
The shift that both households and businesses are making from landlines to VoIP phone systems is mainly due to the benefits and features now available (displayed below).
How a VoIP Telephone is Different from a Landline Phone:
There are several differences between the two systems – from technological contrasts pricing and scalability.
Here is a list of major differences that will help you better understand VoIP vs. landlines.
Feature |
VoIP |
Landline |
| Setup cost | Low | High |
| Running cost | Low | High |
| KBPS | Needs 10 KBPS | Needs 64 KBPS |
| Multimedia | Transmit voice, video, and any form of multimedia just like you do on the internet | No support for multimedia. Only voice |
| Scalability | Easy and inexpensive to scale as your business grows | Additional phone sets and wired phone lines needed in order to scale. Not easy-to-scale |
| Add-ons | The large number features available at no additional cost (call waiting, forwarding, call parking, etc.) | Limited options for add-ons, most of which cost extra |
| Outages | Internet should be functional at all times, but calls can be forwarded to a secondary device during a power outage | Usable during a power outage |
| Call pricing | Free VoIP to VoIP calls. International and mobile calls typically charged at a nominal rate | No free PSTN to PSTN calls. All calls are charged |
In-Depth Comparison
Let’s get into the nitty-gritty of VoIP vs. landlines:
1. Features
Landlines
A landline is a telephone connected to copper wires. These wires run underground and connect to every other landline phone across the world through networks, also known as a PSTN or POTS. This communication method has been around since the 1800s and is considered quite reliable. One of the prominent features of using a landline phone is that it is a tried and tested technology that has proven its stability over the years.
Once you have a landline phone in your office, you can sit back and relax because it will connect without problems. Power outages don’t impact a landline’s connectivity unless you’re using a cordless device.
Beyond reliability, here are some key features of a landline:
- Secure and stable.
- 100% uptime.
- Minimal maintenance. Once you have a phone set, you can use it for years. (Note: this excludes on-premise PBX systems which do require extensive maintenance)
- Call forwarding, voicemail, call conferencing, and several other features are available with your landline connection; but they come at a cost.
VoIP
In terms of features, landlines are no match against VoIP. If you prefer having more control over your calling experience, VoIP telephones are your best bet.
With VoIP, you can use your mobile phone, computer, or desk phone to make phone calls; the device only needs a stable Internet connection.
Here are some of the most popular features and benefits from today’s VoIP phone systems:
- Mobility and portability. This is what makes VoIP a perfect choice for businesses. You don’t have to be in your office to make or receive phone calls.
- Auto-attendants
- Call forwarding
- Call recording
- Call analytics
- Voicemail to email messaging
- Voicemail to text
- Anonymous call rejection
- Softphone capabilities. Essentially you can turn any device into a phone. This includes everything from your mobile device to your tablet or laptop.
- Business integrations. VoIP phone system can be integrated with several third-party tools and software such as your CRM tool, sales software, or email marketing software.
- Scalability. Adding lines doesn’t require additional copper wiring or on-premise changes.
Verdict
VoIP comes with features that you cannot even think of getting with a landline. As far as features are concerned, VoIP is definitely a clear winner.

2. Cost
Landlines
Look at your last phone bill. It likely isn’t cheap. This is often a deciding factor in the debate of VoIP vs. landlines. As the owner of a business, you’d love to save on costs. And unfortunately, landlines don’t help you much there.
Let’s begin by looking at the setup fee. This alone is normally under $100. Then add in the monthly fee (going as high as $100 per line), and expenses quickly add up. If you need, say, 10 lines for your business, you could be spending as much as $1,000 each month because each line is considered unique.
If you need additional functions or features for your telephone system such as intercom, call transfer, call queuing, etc., you’ll need to install a Private Branch Exchange (PBX). This is a private telephone network that you’ll control and manage in-house.
A PBX can cost you a few thousand dollars. Additionally, you’d need an expert to install it and visit to fix inevitable issues.
Sounds expensive? It is.
This is why most businesses switch to VoIP phone systems.
A prime example of a company that has done this is JTG/Muir, a manufacturing supplier based in California. According to PC World, JTG/Muir switched from a PBX to VoIP due to a lack of features and hefty maintenance costs. As a result, the company is now saving $1,200 a month, is enjoying better features, and has 3x the bandwidth of its previous PBX system.
Hundreds of thousands of companies across the country have experienced savings similar to JTG/Muir. Data compiled from all these companies shows that switching to VoIP from a landline or PBX system can save businesses up to 60 perfect each month.
VoIP
With the potential of 60 perfect savings, you can’t go wrong. If you want to save on costs, go with VoIP.
Verdict
In terms of cost, VoIP beats landlines by a landslide. Shifting to VoIP can give your business a competitive edge over competitors that are still using traditional systems. A clear win.
3. Reliability
Reliability is defined as being trustworthy or performing consistently well.
Let’s see how landlines vs. VoIP deal with reliability:
Landline
Landlines are reliable because, as a customer, you get a separate line for each connection, resulting in consistent performance.
But in the long-run, landlines (PSTNs) aren’t reliable.
Why?
Because landlines are becoming obsolete. People have already stopped using them. In today’s mobile-driven world as much as 40 percent of U.S. households don’t have a landline. As a result, telecom companies are losing 700K landline customers a month.
AT&T, which has the biggest landline network, said:
“Our current infrastructure has served us well for almost a century but it no longer meets the needs of America’s consumers. The transition to broadband and IP services that have already begun is driven by consumers who are moving to the Internet and choosing to connect in ways not imagined just a decade ago.”
This shows that landlines don’t have the potential to ‘perform consistently well’ to the point that it meets the needs of its users. Your landline might be reliable today, but it may not be reliable a few years down the road.
VoIP
VoIP is reliable. And it has the potential to perform consistently well for years to come.
Why?
Because it is evolving as opposed to the landline that didn’t change since its invention. As long as VoIP continues to evolve and grow, it will stay reliable.
The VoIP industry is expected to reach $140 billion by 2021. This shows that telephone companies and businesses are already investing in VoIP.
VoIP phone systems have well over 99.99 percent uptime (time in which the system is in operation). Broadband, 4G and now 5G are there to make your internet stable and reliable which leads to improvement in the overall VoIP phone system.
Just think about how this could impact your business. Statistics show that businesses that switch to VoIP save up to 32 minutes per day per employee because staff can now reach people on the first try.

Even if your call gets dropped it is immediately transferred to your voicemail or routed to a peer. It all comes down to what features you have enabled to deal with call disconnection.
Think of VoIP as a long-term investment. It will only get better with the passage of time.
Verdict
Landlines used to be reliable but they aren’t being invested in anymore. They are becoming obsolete. VoIP, on the other hand, is where the telecom sector is investing heavily and is far more reliable in terms of call connectivity and long-term reliability.
VoIP takes the lead again.
4. Technology
Both landlines and VoIP use different technologies. But how do the two technologies work, and which one is better?
Landline
Landlines work via circuit switching through a Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN).
In order to connect one phone to another, the phone call is moved from several switches at local, regional, national, and international levels. This is known as ‘routing.’ A PBX uses extensions from main phone numbers for routing within an organization.
The phone number or extension serves as a coded map for routing a call. As soon as you dial a number, it moves through multiple switches and reaches the destination within a few seconds. The first three digits of a landline number represent the area code; the next three digits are the exchange, and the last four digits represent the subscriber number.
Here is how it works at the backend:

- Your landline telephone set converts your voice into electrical signals which are then transmitted to the terminal via cable.
- The terminal is responsible for sending the electrical signal (your call) to the central office. The electrical signal is decoded, and the call is then routed to the relevant exchange immediately.
- Next, a tandem office is used to transmit the electrical signal to a distant central office.
- When the signal is received at the right central office it is routed to the correct terminal.
- Finally, the terminal routes the call to the desired number, and the phone converts the electrical signal back to sound waves.
This technology itself relies on a complex network of cables. In today’s wireless age, this has become a dated technology. This is one reason why landlines aren’t considered quite as reliable in the long-run.
VoIP
VoIP works differently because it uses the Internet for all communications. Your phone is connected to the Internet through your network, and when you make a call, data from your device is transferred in the form of data packets across the web.
Here is how it works:
- The voice signals are converted into packets of data.
- These packets travel through the internet to the VoIP provider and reach the destination.
- Your VoIP provider then uses the cloud-based PBX to route the call.
- From the hosted PBX call data can be sent to any landline or VoIP phone.
- Once the data reaches its destination, it reassembles and converts
- back into voice signals.
This is wireless technology that is here to stay. VoIP technology isn’t just new and updated; it’s the modern way businesses are communicating with customers around the world.
Verdict
VoIP once again takes the lead as it uses updated technology. The Internet is not going anywhere, and neither is VoIP. Landline technology is clearly a thing of the past.
Final Verdict
So what will you choose for your business: VoIP or landlines?
VoIP is superior to landlines in terms of features, cost, reliability, and technology. This is why the VoIP services market is expected to expand 10 percent every year until 2021. You won’t see any such growth opportunity for landlines.

How to Switch from a Landline to VoIP
If you’re using a landline for your business, you have two choices:
- Continue using a landline phone system.
- Shift to VoIP so you can reduce cost, enjoy better features, and improve corporate communication.
The logical choice based on what is discussed above should be to switch to VoIP — immediately.
Guess what, it is easy to switch!
Prerequisites
Before you can proceed with the transition, there are certain prerequisites:
- A reliable internet service provider
- SIP-enabled device
- VoIP provider
1. Internet Service Provider
Since VoIP uses the Internet to make and receive calls, you must have a reliable Internet connection.
In order to make sure you can easily use your VoIP phone system, you need to have enough bandwidth. Ensure of your ISPs upload and download speeds meet industry standards so as to avoid any hiccups.
- Calculate the number of total devices that you need for your business. Each VoIP device consumes a certain portion of the bandwidth, so stick with what you actually need.
- Generally, you need 100kbps or 0.1mbps for one VoIP device. If you need 5 devices, you’d need an additional 500kbps.
- Use our VoIP speed test tool to check your Internet speed and network jitter levels.
If you’re using a high-speed broadband connection, speed won’t be an issue. But you don’t want your network to run at maximum capacity all the time, so it’d be best to contact your ISP and upgrade your internet plan.
 2. SIP-enabled Device
2. SIP-enabled Device
A Session Initiated Protocol (SIP) enabled device is used to set up and manage phone calls. In order to leverage all of the benefits VoIP has to offer you will need to get SIP-enabled phones for your staff. The number of phones needed is based on the number of employees who need to be using a phone at any given time.
You have two options to choose from:
- Convert your existing analog telephone to a SIP phone with an ATA adapter.
- Purchase a hard phone. Hard phones are similar to traditional phones but let you connect to the network. You can easily get a SIP-enabled hard phone under $100.
You can also use a softphone which lets you make and receive phone calls from your computer, smartphone or a tablet. It works like an app.
3. VoIP Provider
Once you have the Internet and the devices you’ll need a VoIP provider who will set up your VoIP phone network and will help you get started.
We can help you with that.

 2. SIP-enabled Device
2. SIP-enabled Device